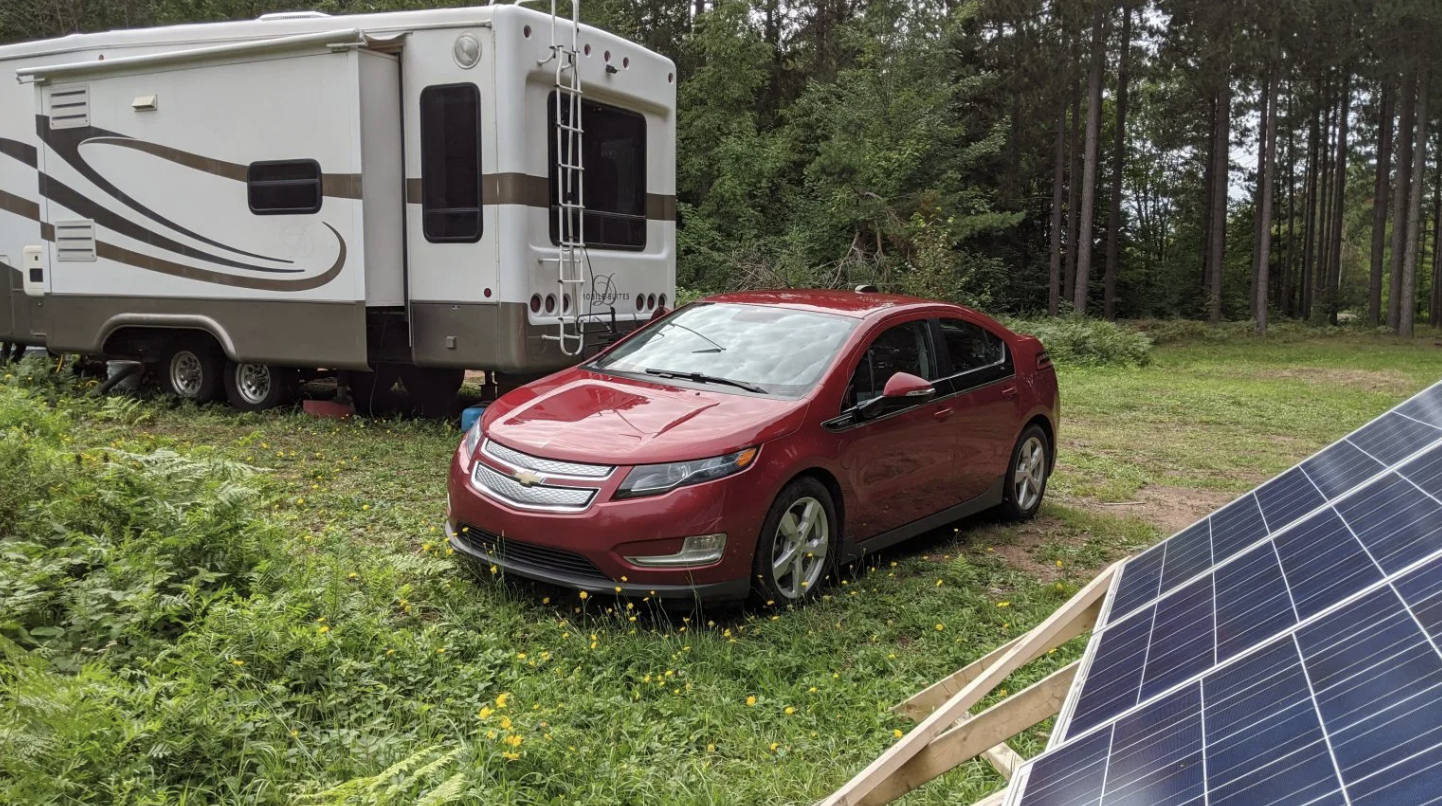
Best Cars to Use – Plug-in Hybrid / Full Electric
There are many great plug-in hybrid vehicles available in the market, and the best one for you will depend on your specific needs and preferences. However, here are some of the top plug-in hybrids based on various factors:
- Best overall: Toyota Prius Prime
- Best luxury plug-in hybrid: BMW 330e
- Best plug-in hybrid SUV: Ford Escape Plug-In Hybrid
- Best plug-in hybrid with the longest electric range: Hyundai Ioniq Plug-In Hybrid
- Best plug-in hybrid with AWD: Subaru Crosstrek Hybrid
Other notable plug-in hybrids include the Chevrolet Volt, Kia Niro Plug-In Hybrid, Mitsubishi Outlander Plug-In Hybrid, and the Volvo XC60 T8.
It’s important to do your research and consider factors such as driving range, charging options, performance, and price when choosing a plug-in hybrid that’s right for you.
Range from Solar – Range you need – Battery size
Here are some of the best plug-in hybrids and their electric-only range:
- Toyota Prius Prime: 25 miles
- Hyundai Ioniq Plug-In Hybrid: 29 miles
- Ford Escape Plug-In Hybrid: 37 miles
- BMW 330e: 22 miles
- Volvo XC60 T8: 18 miles
- Mitsubishi Outlander Plug-In Hybrid: 24 miles
- Kia Niro Plug-In Hybrid: 26 miles
- Subaru Crosstrek Hybrid: 17 miles
It’s worth noting that the range can vary depending on factors such as driving style, weather, and terrain. However, these plug-in hybrids offer a good balance between the electric-only range and the traditional gasoline engine range, making them a great choice for those who want to reduce their fuel consumption and emissions while still having the flexibility of a gasoline engine.
Equipment needed for the RV or Travel Trailer – Minimum requirements for your vehicle
To charge an electric vehicle using solar power, you will need the following solar equipment:
- Solar Panels: Solar panels are the primary component of a solar charging system. The number of solar panels you need will depend on the size of your EV battery and the amount of sunlight in your area.
- Inverter: An inverter is necessary to convert the direct current (DC) power generated by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) power that can be used to charge your EV.
- Charge Controller: A charge controller regulates the amount of electricity that flows from the solar panels to the EV battery, preventing overcharging and extending the life of the battery.
- Battery Bank: A battery bank stores the excess solar power generated during the day for use during the night or when there is not enough sunlight available to charge the EV.
- Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE): An EVSE is a device that connects your EV to the solar charging system. It regulates the flow of electricity and ensures safe and efficient charging.
It’s important to note that installing a solar charging system for an EV requires professional installation and may require permits and approvals from local authorities. Additionally, the cost of installing a solar charging system can vary widely depending on the size of the system, the type of equipment used, and the complexity of the installation.
Level 1 Charging – 120v ( about 5 miles per hour charged) at 12 amps(1440 watt hour)
Level 1 EV charging refers to the simplest and slowest method of charging an electric vehicle. It involves using a standard 120-volt electrical outlet, which is commonly found in homes and businesses. Level 1 charging equipment comes standard with most electric vehicles, and it typically includes a charging cord with a standard 120-volt plug on one end and a connector that plugs into the vehicle’s charging port on the other end.
Level 1 charging is slow because it can provide a maximum charging rate of only 1.4 kW. This means that it can take several hours or even overnight to fully charge an electric vehicle’s battery, depending on the battery size and the starting state of charge. For example, charging a typical electric vehicle with a 60 kWh battery from empty to full using Level 1 charging could take up to 44 hours.
Despite its slow charging rate, Level 1 charging can be convenient for many EV owners because it can be done using a standard household outlet, which is widely available. Level 1 charging is also the least expensive option for EV charging, as it does not require any special charging equipment or installation.
However, Level 1 charging may not be practical for all EV owners, especially those who need to charge their vehicles quickly or who have larger battery capacities that require more charging time. In those cases, Level 2 or DC fast charging may be more suitable.